Vitamin A is an essential nutrient that plays a major role in eye health. It can help protect against serious vision problems, like night blindness and age-related macular degeneration.

In this article, we’ll discuss why you need vitamin A for healthy vision and the best sources to get it from. We’ll also look at how much of this vital nutrient you should consume daily to ensure optimal eye health.
So if you’re concerned about your vision now or in the future, read on to learn more about the importance of getting enough vitamin A!
What Is Vitamin A?
Vitamin A is an essential micronutrient for healthy vision and other important bodily functions. It’s a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it can be stored in the body for later use, as opposed to water-soluble vitamins like B and C, which must be replenished more frequently.
Vitamin A is commonly found in many dietary supplements and foods that come from animals or plants; retinol is the form of Vitamin A found in animal products, while carotenoids are found in plant sources. Vitamin A helps prevent night blindness, an eye disorder caused by insufficient amounts of this nutrient, but it also supports immune function, cell growth, and gene expression.
Retinol is the most active form of Vitamin A available through dietary intake and supplementation. Animal products such as egg yolk, liver, fish oil, fortified milk, and butter all contain some level of retinol. Know more about the differences between Vitamin A and Retinol.
Carotenoids – another vitamin supplement – are provitamin forms converted into retinol once consumed. Beta-carotene (found in dark green vegetables) has been discovered to convert at twice the rate compared to alpha-carotene (from yellow/orange fruits). Other carotenoid sources include sweet potatoes, carrots, apricots, and cantaloupes.
The benefits derived from consuming adequate levels of Vitamin A vary with age; infants need enough to support normal development while adults require less overall due to its storage capacity within the body’s tissues.
With that said however, deficiency remains prevalent among both groups as well as children needing sufficient supply for proper growth and maturation processes against disease susceptibility – especially considering modern diets don’t always provide balanced nutrition requirements across all essential nutrients.
Moving on: let’s explore different sources where one can obtain their daily dose of Vitamin A!
Sources Of Vitamin A
When it comes to healthy vision, vitamin A plays an important role! This essential nutrient can be easily obtained from a variety of sources. In fact, many delicious and nutritious foods contain high levels of the vitamin. Let’s take a look at some of them!
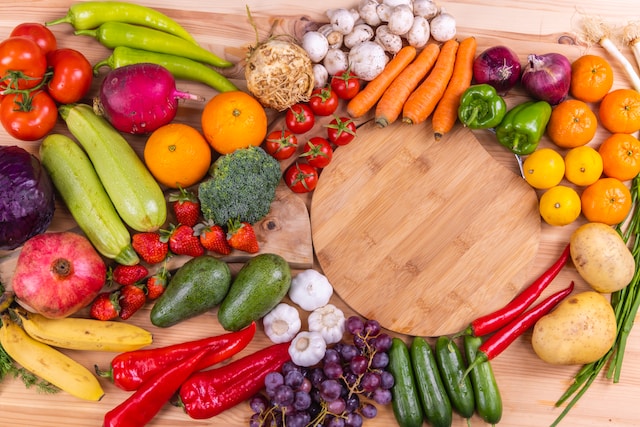

Vitamin A-rich foods include:
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale
- Carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkins, cantaloupe and apricots
- Dairy products like milk and yogurt
- Eggs
- Fish such as tuna, salmon, or mackerel
- Liver
- Fortified cereals
- Orange peppers
These fruits and vegetables are packed with carotenoid pigments such as beta-carotene that convert into retinol in our bodies – an active form of vitamin A. Therefore, eating these foods will give you plenty of the vitamins your body needs for optimum eye health.
With just a few dietary tweaks, you can ensure your eyes stay in top shape all year round! Now let’s move on to explore the benefits of having adequate amounts of Vitamin A in your diet.
Benefits Of Vitamin A
In addition to its role in creating skin cells and proper immune system functioning, Vitamin A is also essential for healthy eye function. With adequate amounts of Vitamin A, our visual acuity can be maintained at a high level and help prevent common eye diseases.
The benefits that Vitamin A provides for our eyes are numerous:
- Improved Visual Acuity: When consumed regularly, Vitamin A helps maintain sharp vision by helping us adjust to different levels of light and contrast.
- Night Vision: It further improves night vision by reducing glare from lights or oncoming headlights while driving in the dark.
- Color Perception: Furthermore, it plays an essential role in color perception, allowing us to accurately differentiate between colors.
- Eye Disease Prevention: Vitamin A has been linked with decreased risk of developing macular degeneration (AMD), cataracts, glaucoma, and other age-related eye conditions due to its antioxidant properties which protect against oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
By including foods rich in Vitamin A in our diet, we can ensure optimal health and functionality of our eyes over time – something that’s especially relevant when considering the damaging effect of UV radiation exposure on our long-term ocular health.
Onwards then to exploring sources of this essential nutrient!
Foods High In Vitamin A
Vitamin A is essential for healthy vision and can be found in various forms of food.
- Fish is an excellent source of vitamin A, with canned tuna fish containing approximately 1296 international units (IU) per 3-ounce serving.
- Vitamin A vegan sources include carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach.
- Eating one cup of cooked carrots provides over 200 percent of the daily recommended value of this nutrient.
- Fruits high in vitamin A include cantaloupe and apricots – eating just one medium-sized cantaloupe will fulfill your daily requirement.
For those looking to increase their intake of vitamin A further than what can be obtained through diet alone, taking a supplement may help reach optimal levels.
Vitamin A Supplements
Vitamin A plays a vital role in vision health. It is essential for regenerating the retina, an integral part of healthy eyesight.
There are several ways to get vitamin A into your system; through food sources like sweet potatoes and dark leafy greens or by taking eye health supplements.
Supplements exist as preformed vitamin A (retinol) or beta-carotene, which can convert to active form when needed. Retinol is more effective at increasing serum concentrations than its plant-based counterpart, beta-carotene.
Additionally, it has been reported that consuming high doses of beta-carotene can actually interfere with retinal regeneration due to increased oxidative stress within the body.
Thus, when looking for a supplement to improve vision health and support healthy eyesight, choose one containing natural forms of vitamin A, such as retinol, instead of beta-carotene. From there, you’ll have a better chance of achieving optimal levels of this vital nutrient for retinal regeneration and overall eye health.
Moving forward, the prevention of night blindness requires further attention to diet and supplementation choices.
Prevention Of Night Blindness
It’s no secret that having a good vision is essential. Without it, daily tasks such as reading and driving become difficult. That’s why it’s essential to understand the importance of vitamin A for healthy vision.
Vitamin A from fish oil helps prevent night blindness, age-related macular degeneration, and other eye nutrition issues. Our bodies don’t produce enough vitamin A alone, so we need to get it through our diets or supplements.

Eating foods high in vitamin A, like cod liver oil, can help you meet your recommended dietary allowance (RDA). Other sources include carrots, sweet potatoes, kale, spinach, collard greens, cantaloupe, and pumpkins. A multivitamin supplement may also provide the necessary amount of vitamin A if eating these foods does not fit into one’s diet.
Research has shown that vitamin A supplements can improve visual acuity when deficiencies present due to poor nutrition or medical conditions. While getting adequate amounts of this nutrient is important for maintaining optimal health – especially eye health – caution should be used when considering supplementation since excessive intake could lead to toxicity symptoms.
With this in mind, transitioning into understanding what retinol sources exist is key to keeping eyes healthy and seeing clearly well into old age.
Related Post: 5 Ways to Increase the Success Rate of Your Ortho-K Therapy
Retinol Sources
It’s no secret that Vitamin A is essential for healthy vision, but why? As it turns out, this critical nutrient plays a major role in eye health maintenance.
Not only does it help prevent various nutrient deficiencies, but its antioxidant properties also protect the eyes from damage caused by free radicals.
The human body needs Vitamin A to produce rhodopsin – a pigment found in the eye’s retina that helps us see in low light conditions. This vital vitamin also keeps our cornea (the clear tissue at the front of the eye) moist and healthy.

Additionally, Vitamin A can reduce inflammation and dryness while helping with night blindness.
These are just some of the many benefits associated with getting adequate amounts of Vitamin A into your diet – something that should not be overlooked when considering ways to ensure optimal eye health. With proper nutrition, you can maintain healthy eyesight and enjoy all that life has to offer!
Transitioning now into how these important nutrients support healthy eye function…
Healthy Eye Function
Retinol, or Vitamin A, has long been known to have positive effects on vision. Not only is it essential for healthy eyesight and ocular health, but it also provides a range of other benefits.
In this section, we’ll discuss the importance of including Vitamin A in your diet as part of an overall strategy to maintain optimal eye function.
Vitamin A plays an important role in maintaining good ocular health and protecting against age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The nutrient helps to protect retinal cells from damage by oxidative stress and inflammation. It also promotes normal growth and development of the visual system.
As one of the most essential nutrients for vision, adequate amounts are necessary for the proper functioning of our eyes.
In addition to its protective roles, Vitamin A can help improve night vision and color perception. It may also reduce the risk for certain types of cataracts. Studies suggest that consuming foods rich in Vitamin A supports healthy vision and improves general well-being when consumed regularly as part of a balanced diet.
With these potential benefits in mind, let’s look at some carotenoid pigments found naturally within various fruits and vegetables, which provide us with dietary sources of vitamin A.
Carotenoid Pigments
It’s essential to ensure that your eyes are functioning properly and maintaining healthy vision, so it’s necessary to understand the role of vitamin A in achieving this.
This powerful nutrient is found in oil-based foods such as salmon, although these sources may not always be available. Fortunately, there are other ways to get enough vitamin A – specifically from carotenoid pigments.
Carotenoid pigments provide various health benefits for our bodies, including protection against age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Our bodies can absorb these pigments when we eat foods like carrots or sweet potatoes – both rich in beta-carotene, which converts into Vitamin A once inside the body.
As an added bonus, many plants also contain high amounts of lutein and zeaxanthin which help protect our retinas.
The primary benefit of getting adequate levels of Vitamin A comes down to how it helps maintain eye health over time. It has been shown to reduce the risk of developing AMD and cataracts while improving night vision and overall visual acuity.
Taking steps towards identifying dietary sources of Vitamin A is key for preserving healthy eyesight far into the future. With this knowledge in hand, let’s look at how proper maintenance can keep our eyes strong and vibrant.
Eye Health Maintenance
Carotenoid pigments are important components of a healthy diet and can play an essential role in maintaining good vision.
Vitamin A, specifically, is critical for eye health by helping to support the retina—the layer at the back of the eye that detects light and color. Without it, cells within the retina cannot function properly and may die off over time.

Vitamin A deficiency has been linked to dry eyes, night blindness, cataracts, glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and other sight-related problems.
Fortunately, many common foods contain vitamin A or its precursor beta-carotene, such as sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, cantaloupe melon, kale, and apricots. Regularly eating these nutritious fruits and vegetables will ensure your body gets enough vitamin A for optimal eye health.
Regularly consuming food sources of beta carotene can also help protect against oxidative damage from free radicals, which can cause cell death in the eyes leading to vision loss.
Additionally, supplementing with fish oil containing omega-3 fatty acids like EPA and DHA has been shown to improve overall eye health and reduce inflammation which could put you at greater risk for AMD later in life.
Taking steps now to maintain good eye health through balanced nutrition can pay dividends down the road!
Conclusion
Vitamin A is essential for healthy vision. It helps us to see in low light and keeps our eyes functioning properly.
We should be sure to get enough of this vital vitamin from food sources like sweet potatoes, carrots, and dark leafy greens or by taking a supplement if necessary.
Eating foods high in Vitamin A and maintaining regular eye health checks ensures that our vision remains clear and sharp as we age.
Taking care of your eyes today will help you have better vision tomorrow!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can vitamin A improve vision?
Vitamin A can improve vision if you have a deficiency of this nutrient, but it will not improve vision beyond normal levels if you already have adequate vitamin A levels.
Is vitamin A important for normal vision?
Yes, vitamin A is essential for normal vision because it is needed to produce a pigment called rhodopsin in the retina of the eye.
Which vitamin A is needed to promote vision?
The form of vitamin A needed for promoting vision is called retinol.
Can vitamin A prevent some vision problems?
Vitamin A can help prevent vision problems such as night blindness and age-related macular degeneration.
Is it OK to take vitamin A every day?
It is generally safe to take vitamin A daily as long as you do not exceed the recommended daily intake.
What are 2 symptoms of vitamin A deficiency?
Two symptoms of vitamin A deficiency are night blindness and dry eyes.
How much vitamin A should I take daily?
The recommended daily intake of vitamin A is 900 micrograms for men and 700 micrograms for women.
What is the best form of vitamin A?
The best form of vitamin A is retinol, which is found in animal sources such as liver, eggs, and dairy products.
Does lack of vitamin A cause loss of vision?
Yes, lack of vitamin A can cause loss of vision, particularly night blindness.
Which fruit has most vitamin A?
Mangoes are one of the fruits that have the most vitamin A, with one cup of sliced mango containing about 25% of the daily recommended intake.
How much vitamin A is too much?
Consuming more than 3,000 micrograms of vitamin A per day can be toxic and lead to adverse health effects.
Can too much vitamin A damage your eyes?
Yes, consuming too much vitamin A can damage your eyes and cause vision problems.
Is vitamin A good for dry eyes?
Yes, vitamin A can be beneficial for dry eyes because it helps maintain the health of the outer protective layer of the eye.
References
- National Institutes of Health. Vitamin A Fact Sheet for Consumers. (2021). https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminA-Consumer/
- American Optometric Association. Nutrition and Age-Related Macular Degeneration. (2021). https://www.aoa.org/patients-and-public/caring-for-your-vision/nutrition/nutrition-and-amd
- Mayo Clinic. Vitamin A. (2021). https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-vitamin-a/art-20365945
- MedlinePlus. Vitamin A. (2021). https://medlineplus.gov/vitamina.html